Drug Details
| General Information of the Drug (ID: DR9957) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name |
Ampicillin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
69-53-4; Ampicillin; Aminobenzylpenicillin; Ampicillin acid; Amcill; Polycillin; Principen; Omnipen; Ampicilline; Penbritin; Pentrexyl; Synpenin; Tokiocillin; Totacillin; Novo-ampicillin; D-Ampicillin; Ampicillin Anhydrous; D-(-)-Ampicillin; Adobacillin; Amblosin; Ampichel; Ampicilina; Ampicillinum; Ampifarm; Ampipenin; Ampiscel; Amplacilina; Amplipenyl; Amplisom; Amplital; Bonapicillin; Britacil; Campicillin; Copharcilin; Delcillin; Divercillin; Doktacillin; Duphacillin; Grampenil; Guicitrina; Lifeampil; Norobrittin; Orbicilina; Penbristol; Penbrock; Penicline; Pentrexl; Princillin; Racenacillin; Rosampline; Roscillin; Semicillin; Servicillin; Sumipanto; Texcillin; Totalciclina; Trifacilina; Ultrabion; Ultrabron; Viccillin; Acillin; Amfipen; Ampicil; Ampikel; Ampimed; Ampisyn; Ampivax; Ampivet; Amplin; Binotal; Morepen; Nuvapen; Penimic; Pensyn; Pentrex; Ponecil; Tolomol; Totapen; Vampen; Cimex; Supen; anhydrous ampicillin; Ampicillin anhydrate; Pfizerpen A; Amipenix S; Ampi-bol; SK-Ampicillin; Amfipen V; Pen Ampil; QIDamp; Ampi-Tab; D-Cillin; Olin Kid; Ro-Ampen; Ampi-Co; Austrapen; Pen A; Ampicillina [DCIT]; Bayer 5427; D-(-)-alpha-Aminobenzylpenicillin; ABPC; Ampicilina [INN-Spanish]; Ampicilline [INN-French]; Ampicillinum [INN-Latin]; Ampicin; D-(-)-alpha-Aminopenicillin; Deripen; Wypicil; Alpen; Ampicillin A; Polycillin-N; Totacillin-N; Penbritin-S; AY-6108; Omnipen-N; BRL 1341; Penbritin syrup; Semicillin R; D-(-)-6-(alpha-Aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic acid; P-50; KS-R1; Penbritin paediatric; NSC-528986; AB-PC; BRL-1341; 6-(D(-)-alpha-Aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic acid; Guicitrine; Ampen; NSC 528986; AB-PC Sol; Ampicillin, anhydrous; UNII-7C782967RD; C16H19N3O4S; CHEBI:28971; MFCD00005175; Alpha-Aminobenzylpenicillin; 6-(D-(2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido))-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; MLS000028405; (2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; Ampicillina; HI 63; Ukapen; Pfizerpen-A; WY-5103; AMPI; 7C782967RD; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; P 50; SQ 17382; Penicillin, (aminophenylmethyl)-; SMR000058352; Ampicillin Base; DSSTox_CID_2602; AY 6108; DSSTox_RID_76654; DSSTox_GSID_22602; (2S,5R,6R)-6-((R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-2-Amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; Polyflex (Veterinary); ampicillanyl; Ampicillin [USAN:BAN:INN:JAN]; CAS-69-53-4; (2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-AMINO-2-PHENYLETHANOYL]AMINO}-3,3-DIMETHYL-7-OXO-4-THIA-1-AZABICYCLO[3.2.0]HEPTANE-2-CARBOXYLIC ACID; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid,6-[[(2R)-aminophenylacetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, trihydrate,(2S,5R,6R)-; Omnipen (TN); Totacillin (sodium); BA 7305; HSDB 3009; AMPICILLIN/AMPICILLIN TRIHYDRATE; Ampicillin (USP/INN); EINECS 200-709-7; vidopen; Vidocillin; Marcillin; Pentritin; NSC528986; D-(-)-.alpha.-Aminobenzylpenicillin; Ampicillin,(S); NCGC00018160-02; (2s,5r,6r)-6-((r)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenyl-acetyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-((aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2S-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta(S*)))-; Ampicillin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Ampicillin (anhydrous); Spectrum_000050; 1h8s; AY 6108; D-a-Aminobenzylpenicillin; Opera_ID_1630; Prestwick0_000114; Prestwick1_000114; Prestwick2_000114; Prestwick3_000114; Spectrum2_000769; Spectrum3_000301; Spectrum4_000149; Spectrum5_000814; CHEMBL174; Epitope ID:115008; Epitope ID:116057; EC 200-709-7; SCHEMBL3526; BSPBio_000128; BSPBio_001862; KBioGR_000598; KBioSS_000430; Anhydrous ampicillin (JP17); MLS001074168; BIDD:GT0184; DivK1c_000466; SPBio_000818; SPBio_002067; Ampicillin, analytical standard; BPBio1_000142; DTXSID4022602; CHEBI:53713; GTPL10896; KBio1_000466; KBio2_000430; KBio2_002998; KBio2_005566; KBio3_001362; NINDS_000466; HMS2090I11; HMS2233H23; Ampicillin acid; Principen; Amcill; HY-B0522; ZINC3830218; Tox21_113049; Tox21_301416; BDBM50350465; SBB063111; AKOS015888156; Tox21_113049_1; AC-8805; DB00415; VA10275; WY 5103; 6beta-[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-2,2-dimethylpenam-3alpha-carboxylic acid; IDI1_000466; SMP1_000211; NCGC00023282-05; NCGC00023282-06; NCGC00023282-21; NCGC00178944-03; NCGC00248937-01; NCGC00255127-01; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-(2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, D-(-)-; ST077148; SBI-0051283.P003; 6-(a-Aminophenylacetamido)penicillanic acid; C06574; D00204; AMPICILLIN ANHYDROUS, PHARMACEUTICAL GRADE; Q244150; 6-D(-)-alpha-Aminophenylacetamido-penicillanic acid; BRD-K68432770-001-08-0; Ampicillin, anhydrous, 96.0-100.5% (anhydrous basis); Ampicillin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Anhydrous ampicillin, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Ampicillin, anhydrous, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; (2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-AMINO-2-PHENYLETHANOYL]AMINO}-3,3-DIMETHYL-7-OXO-4-THIA-1-AZABICYCLO[3.2.0]HEPTANE-2-CARBOXYLIC; 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 6-(((2R)-aminophenylacetyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-, (2S,5R,6R)-; 6-((2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetylamino)(2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid; 6-((2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetylamino)(2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-aza bicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, oxamethane, oxamethane, oxamethane; 6-[(Aminophenylacetyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 9CI; AMPICILLIN; D(-)-ALPHA-AMINOBENZYLPENICILLIN; 6-[D(-)-ALPHA-AMINOPHENYLLACETAMIDO]PENICILLANIC ACID
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Molecular Type |
Small molecule
|
|||
| Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | Approved | [1] | |
| Structure |
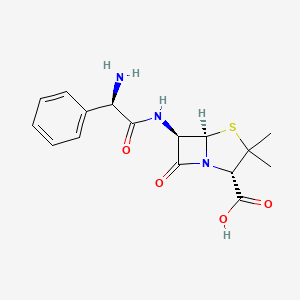
|
Click to Download Mol2D MOL |
||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Natural Product | ||||
| Formula |
C16H19N3O4S
|
|||
| PubChem CID | ||||
| Canonical SMILES |
CC1(C(N2C(S1)C(C2=O)NC(=O)C(C3=CC=CC=C3)N)C(=O)O)C
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C16H19N3O4S/c1-16(2)11(15(22)23)19-13(21)10(14(19)24-16)18-12(20)9(17)8-6-4-3-5-7-8/h3-7,9-11,14H,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23)/t9-,10-,11+,14-/m1/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
AVKUERGKIZMTKX-NJBDSQKTSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 69-53-4
|
|||
| ChEBI ID | ||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||
| DrugBank ID | ||||
| Combinatorial Therapeutic Effect(s) Validated Clinically or Experimentally | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α. A List of Natural Product(s) Able to Enhance the Efficacy of This Drug | ||||||
| Amentoflavone | Gingko biloba | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Enterococcus faecium ATCC 19434 | Microorganism model | Enterococcus faecium | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | ||||
| Streptococcus mutans ATCC 3065 | Microorganism model | Streptococcus mutans | ||||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 43895 | Microorganism model | Escherichia coli | ||||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | Microorganism model | Escherichia coli | ||||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | Microorganism model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Amentoflavone had a considerable antibacterial effect and synergistic interaction with antibiotics against various bacterial strains. The formation of hydroxyl radical would be a cause of the synergistic effect and that this oxidative stress originated from a transient NADH depletion. . | |||||
| Bisdemethoxycurcumin | Curcumin | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [3] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| Molecule(s)
Regulation |
Down-regulation | Expression | UL54 | Molecule Info | ||
| In-vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strains | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Antimicrobial effect of BDMC combined with antibiotics was superior to treatment with that of a single agent alone. | |||||
| Retinol | Daucus carota | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [4] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strains | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 33591 | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | ||||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | ||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Rhein in combination with AM or OX could lead to the development of new combinations of antibiotics against MRSA infection. | |||||
| Target and Pathway | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | Molecule Info | [5] | |


