Drug Details
| General Information of the Drug (ID: DR3693) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name |
Lisinopril
|
|||
| Synonyms |
lisinopril; Prinivil; Zestril; 76547-98-3; Linopril; Lysinopril; 83915-83-7; Acercomp; Inhibril; Lisipril; Noperten; Presiten; Sinopril; Tensopril; Acerbon; Carace; Vivatec; Coric; Lisinopril anhydrous; Lisinopril dihydrate; Alapril; Inopril; Lisinal; Lisoril; Lispril; Novatec; Sinopryl; Cipral; Linvas; Lipril; Loril; Prinil; Tensyn; Tersif; Lisinoprilum; Longes; Hipril; UNII-7Q3P4BS2FD; MK-521; Lisinopril (INN); [N2-[(S)-1-CARBOXY-3-PHENYLPROPYL]-L-LYSYL-L-PROLINE; Lisinopril (Zestril); C21H31N3O5; N2-[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-lysyl-L-proline; Zestril (TN); 7Q3P4BS2FD; CHEBI:43755; Lisinopril [INN]; Qbrelis; (S)-1-((S)-6-Amino-2-(((S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino)hexanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; LPR; (S)-1-(N2-(1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-L-proline; Nanopril; Lisinoprilum [Latin]; (S)-1-(N(2)-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-L-proline; MFCD01698825; CHEMBL1237; Lizinopril; Diroton; Lisitec; Lisopril; Listril; Lizonoton; Optimon; Prinvil; Skopryl; Vitopril; Amicor; Doneka; Irumed; Laaven; MLS002154258; MK 521; MK 522; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-{[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino}hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; SMR000544473; CCRIS 3568; SMR001233519; EINECS 278-488-1; BRN 4276619; lysinopryl; (S)-1-[N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline; N-(1(S)-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl-L-proline; N2-((S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl-L-proline; HSDB 6852; (S)-1-(N(sup 2)-(1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-L-proline; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; 77726-95-5; (S)-1-[N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline dihydrate; 1-(N2-(1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-L-proline; L-Proline, N2-((1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl-; Spectrum_000497; 1-[Nalpha-[(S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-lysyl]-L-proline; Prestwick0_000301; Prestwick1_000301; Prestwick2_000301; Prestwick3_000301; Spectrum2_001456; Spectrum3_000941; Spectrum4_001040; Spectrum5_000995; SCHEMBL15680; BSPBio_000262; KBioGR_001599; KBioSS_000977; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-1-hydroxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; MLS001306436; MLS001306481; BIDD:GT0755; DivK1c_001037; SPECTRUM1501217; SPBio_001351; SPBio_002481; BPBio1_000290; GTPL6360; ICI-209K; DTXSID6040537; BDBM66979; HMS503O15; KBio1_001037; KBio2_000977; KBio2_003545; KBio2_006113; KBio3_002002; L-Proline, 1-(N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-; N(2)-[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-lysyl-L-proline; N~2~-[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]-L-lysyl-L-proline; cid_22887897; NINDS_001037; HMS1921B14; HMS2090O14; HMS2092L21; HMS2850N20; Pharmakon1600-01501217; L-Proline, 1-(N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-, (S)-; ZINC3812863; 1835AH; 2517AH; BDBM50367879; CCG-39190; DL-434; KM1776; NSC751176; NSC758151; s2076; AKOS015836369; AKOS015894970; L-Proline, 1-(N(sup 2)-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl)-, (S)-; AB04852; BCP9000856; DB00722; MCULE-7813362088; NSC-751176; NSC-758151; IDI1_001037; NCGC00179623-01; HY-18206; SBI-0051692.P002; L0220; A11876; D08131; 54256-EP2270011A1; 54256-EP2272834A1; 54256-EP2277879A1; 54256-EP2287165A2; 54256-EP2287166A2; 54256-EP2292228A1; 54256-EP2292620A2; 54256-EP2298742A1; 54256-EP2298776A1; 54256-EP2298779A1; 54256-EP2301923A1; 54256-EP2301929A1; 54256-EP2301931A1; 54256-EP2301935A1; 54256-EP2305648A1; 54256-EP2305674A1; 54256-EP2308562A2; AB00052250-13; AB00052250_14; AB00052250_15; 547L983; A838743; Q412208; SR-05000001786; SR-05000001786-1; BRD-K67966701-335-03-5; Z2786051707; N-[N2 (1(S)-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline; N-[N2 -(1(S)-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline; (S)-1-[N2-(1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-lysyl-proline dihydrate; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenyl-propyl]amino]hexanoyl]proline;hydrate; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxohexyl]-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxohexyl]-2-pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid;hydrate; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid;hydrate; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-azanyl-2-[[(2S)-1-oxidanyl-1-oxidanylidene-4-phenyl-butan-2-yl]amino]hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid; (2S)-1-[(2S)-6-azanyl-2-[[(2S)-1-oxidanyl-1-oxidanylidene-4-phenyl-butan-2-yl]amino]hexanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid;hydrate; (S)-1-((S)-6-amino-2-((S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropylamino)hexanoyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Molecular Type |
Small molecule
|
|||
| Disease | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00] | Approved | [1] | |
| Structure |
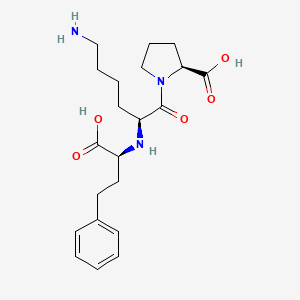
|
Click to Download Mol2D MOL |
||
| ADMET Property |
Absorption Cmax
The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of drug is 58 mcg/L
Absorption Tmax
The time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 6-8 h
BDDCS Class
Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System (BDDCS) Class 3: high solubility and low permeability
Bioavailability
The bioavailability of drug is 25%
Clearance
The renal clearance of drug is 121 mL/min
Clearance
The drug present in the plasma can be removed from the body at the rate of 1.2 mL/min/kg
Elimination
94% of drug is excreted from urine in the unchanged form
Half-life
The concentration or amount of drug in body reduced by one-half in 12.6 hours
Half-life
The concentration or amount of drug in body reduced by one-half in 42 hours
Metabolism
The drug is not metabolised
MRTD
The Maximum Recommended Therapeutic Dose (MRTD) of drug that ensured maximising efficacy and moderate side effect is 1.4092 micromolar/kg/day
Unbound Fraction
The unbound fraction of drug in plasma is 1%
Vd
The volume of distribution (Vd) of drug is 124 L
Vd
Fluid volume that would be required to contain the amount of drug present in the body at the same concentration as in the plasma 0.89 L/kg
Water Solubility
The ability of drug to dissolve in water is measured as 97 mg/mL
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Natural Product | ||||
| Formula |
C21H31N3O5
|
|||
| PubChem CID | ||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(N(C1)C(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)O)C(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C21H31N3O5/c22-13-5-4-9-16(19(25)24-14-6-10-18(24)21(28)29)23-17(20(26)27)12-11-15-7-2-1-3-8-15/h1-3,7-8,16-18,23H,4-6,9-14,22H2,(H,26,27)(H,28,29)/t16-,17-,18-/m0/s1
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RLAWWYSOJDYHDC-BZSNNMDCSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 76547-98-3
|
|||
| ChEBI ID | ||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||
| DrugBank ID | ||||
| Combinatorial Therapeutic Effect(s) Validated Clinically or Experimentally | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α. A List of Natural Product(s) Able to Enhance the Efficacy of This Drug | ||||||
| Carnosine | Homo sapiens | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vivo Model | Male Sprague-Dawley rats were injected i.v. with streptozotocin (STZ) to induce diabetes. | |||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Both carnosine and lisinopril exert distinct beneficial effects in a standard model of diabetic nephropathy. Both drugs administered together combine the respective effects of single treatment, albeit without exerting additive nephroprotection. | |||||
| Target and Pathway | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE1) | Molecule Info | [3] | |
| KEGG Pathway | Renin-angiotensin system | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) | |||
| 3 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) | |||
| Pathwhiz Pathway | Angiotensin Metabolism | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| Reactome | Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| WikiPathways | ACE Inhibitor Pathway | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins | |||

