Drug Details
| General Information of the Drug (ID: DR6366) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name |
Fluconazole
|
|||
| Synonyms |
fluconazole; 86386-73-4; Diflucan; Triflucan; Biozolene; Elazor; Biocanol; Fluconazol; Fungata; Fluconazolum; Flucostat; 2-(2,4-DIFLUOROPHENYL)-1,3-DI(1H-1,2,4-TRIAZOL-1-YL)PROPAN-2-OL; UK 49858; Flusol; Zoltec; 2-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol; UK-49858; 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol; C13H12F2N6O; UNII-8VZV102JFY; 1H-1,2,4-Triazole-1-ethanol, alpha-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-alpha-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-; Pritenzol; Flucazol; Flukezol; Flunizol; Zonal; CHEMBL106; 2-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-propanol; 8VZV102JFY; 2,4-Difluoro-alpha,alpha-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl alcohol; alpha-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-alpha-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol; Alflucoz; Cryptal; Dimycon; Oxifugol; Canzol; CHEBI:46081; Forcan; Syscan; Baten; Mutum; Zemyc; 2-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-1,3-di-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylpropan-2-ol; Fluconazole, 98%; MFCD00274549; difluconazole; NCGC00095089-01; Flunazol; Fluconazol [Spanish]; Fluconazolum [Latin]; Loitin; UK-49,858; DSSTox_CID_627; DSSTox_RID_75701; DSSTox_GSID_20627; FLC; DRG-0005; Diflazon; Fuconal; Triconal; Trican; Diflucan (TN); SMR000471882; CAS-86386-73-4; FLCZ; CCRIS 7211; Fluconazole & hGCSF; DIFLUCAN IN SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.9%; HSDB 7420; SR-01000765440; Fluconazole in sodium chloride 0.9%; DIFLUCAN IN DEXTROSE 5% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Flucoral; 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-di(1,2,4-triazolyl)propan-2-ol; Fluconazole & MC-510,011; Fluconazole (f); Fluconazole,(S); Fluconazole in dextrose 5% in plastic container; 2,4-Difluoro-alpha,alpha-1-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)benzyl alcohol; Fluzon [Antifungal]; Fluconazole [USAN]; KS-1059; Fluconazole [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Fluconazole in sodium chloride 0.9% in plastic container; Fluconazole in combination with MGCD290; Spectrum_001654; DIFLUCAN IN SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.9% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Spectrum2_001607; Spectrum3_001912; Spectrum4_000090; Spectrum5_001277; F0677; MGCD290 and Fluconazole; cid_3365; MG-3290 and Fluconazole; SCHEMBL3151; BSPBio_003504; KBioGR_000360; KBioSS_002134; 123631-92-5; MLS001066394; MLS001165780; MLS001195645; MLS001304713; MLS001306492; MLS006011884; BIDD:GT0799; DivK1c_001030; SPECTRUM1503975; SPBio_001613; ZINC4009; Fluconazole (JP17/USP/INN); DTXSID3020627; BDBM25817; HMS503M21; KBio1_001030; KBio2_002134; KBio2_004702; KBio2_007270; KBio3_003009; NINDS_001030; BAYT006267; HMS1922O10; HMS2090I20; HMS2093M21; HMS2230O22; HMS3259H13; HMS3373I19; HMS3654P15; HMS3715F21; HMS3748G19; Pharmakon1600-01503975; AMY23415; BAYT-006267; BCP28522; Fluconazole 2.0 mg/ml in Methanol; HY-B0101; 1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol; Tox21_111419; Tox21_202240; Tox21_300581; 2-(2,4-Difluoro-phenyl)-1,3-bis-[1,2,4]triazol-1-yl-propan-2-ol; ABP001077; AC-428; ANW-42860; BBL005614; CCG-39065; CF0055; DL-407; Fluconazole & Human recombinant granulocyte colony stimulating factor; KM2402; NSC754343; NSC758661; s1331; SBB066063; STK619301; AKOS000280854; Tox21_111419_1; CS-1835; DB00196; Fluconazole, >=98% (HPLC), powder; MCULE-8641424658; NC00650; NSC 758661; NSC-754343; NSC-758661; IDI1_001030; NCGC00095089-02; NCGC00095089-04; NCGC00095089-05; NCGC00095089-06; NCGC00095089-07; NCGC00095089-08; NCGC00095089-09; NCGC00095089-10; NCGC00095089-11; NCGC00254412-01; NCGC00259789-01; 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-di(1H-; Fluconazole 100 microg/mL in Acetonitrile; SBI-0051880.P002; AB0008515; UK-049858; FT-0626437; ST51039043; SW199616-2; EN300-53634; C07002; D00322; J10407; AB00052399-07; AB00052399-08; AB00052399_09; AB00052399_10; 386F734; A841625; Q411478; 3-[4-(pyrrolidin-1-ylsulfonyl)phenyl]propanoicacid; Q-201120; SR-01000765440-2; SR-01000765440-4; SR-01000765440-8; UK-49858;UK 49858;UK49858; BRD-K05977355-001-02-6; BRD-K05977355-001-09-1; F2173-0496; Z235354561; Fluconazole, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; 2-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-1,3-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-2-propanol; Fluconazole, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 2-[2,4-bis(fluoranyl)phenyl]-1,3-bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propan-2-ol; Fluconazole, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; Fluconazole for peak identification, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Fluconazole solution, 2.0 mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material; .alpha.-(2,4-Difluorophenyl)-.alpha.-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-ethanol
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Molecular Type |
Small molecule
|
|||
| Disease | Fungal infection [ICD-11: 1F29-1F2F] | Approved | [1] | |
| Structure |
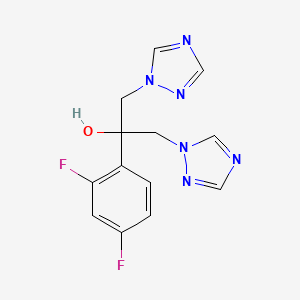
|
Click to Download Mol2D MOL |
||
| ADMET Property |
Absorption Tmax
The time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 3 h
BDDCS Class
Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition Classification System (BDDCS) Class 3: high solubility and low permeability
Bioavailability
The bioavailability of drug is 90%
Clearance
The renal clearance of drug is 14.7 +/- 3.7 mL/min
Elimination
In normal volunteers, fluconazole is cleared primarily by renal excretion, with approximately 80% of the administered dose measured in the urine as unchanged drug
Half-life
The concentration or amount of drug in body reduced by one-half in 20 - 50 hours
Metabolism
The drug is metabolized via the liver
MRTD
The Maximum Recommended Therapeutic Dose (MRTD) of drug that ensured maximising efficacy and moderate side effect is 9.3285 micromolar/kg/day
Unbound Fraction
The unbound fraction of drug in plasma is 0.89%
Vd
The volume of distribution (Vd) of drug is 39 L
Water Solubility
The ability of drug to dissolve in water is measured as 1 mg/mL
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Natural Product | ||||
| Formula |
C13H12F2N6O
|
|||
| PubChem CID | ||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC(=C(C=C1F)F)C(CN2C=NC=N2)(CN3C=NC=N3)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C13H12F2N6O/c14-10-1-2-11(12(15)3-10)13(22,4-20-8-16-6-18-20)5-21-9-17-7-19-21/h1-3,6-9,22H,4-5H2
|
|||
| InChIKey |
RFHAOTPXVQNOHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 86386-73-4
|
|||
| ChEBI ID | ||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||
| DrugBank ID | ||||
| Combinatorial Therapeutic Effect(s) Validated Clinically or Experimentally | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α. A List of Natural Product(s) Able to Enhance the Efficacy of This Drug | ||||||
| Alpinia purpurata lectin | Alpinia purpurata | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus | Microorganism model | Staphylococcus aureus | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Microorganism model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
ApuL-oxacillin combination showed synergistic effect on the oxacillin-resistant isolates UFPEDA-670 and 671, which were not sensitive to lectin alone. | |||||
| Beta lapachone | Tabebuia avellanedae | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [3] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Candida albicans | Microorganism model | Candida albicans | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Beta-lapachone reverted antifungal resistance of S. cerevisiae and C. albicans strains overexpressing CaCdr2p and CaMdr1p transporters by inhibiting these proteins activities. CaCdr2p ATPase activity was not impaired by the compound. | |||||
| Farnesol | Mosla chinensis | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [4] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| Molecule(s)
Regulation |
Up-regulation | Expression | FDFT1 | Molecule Info |
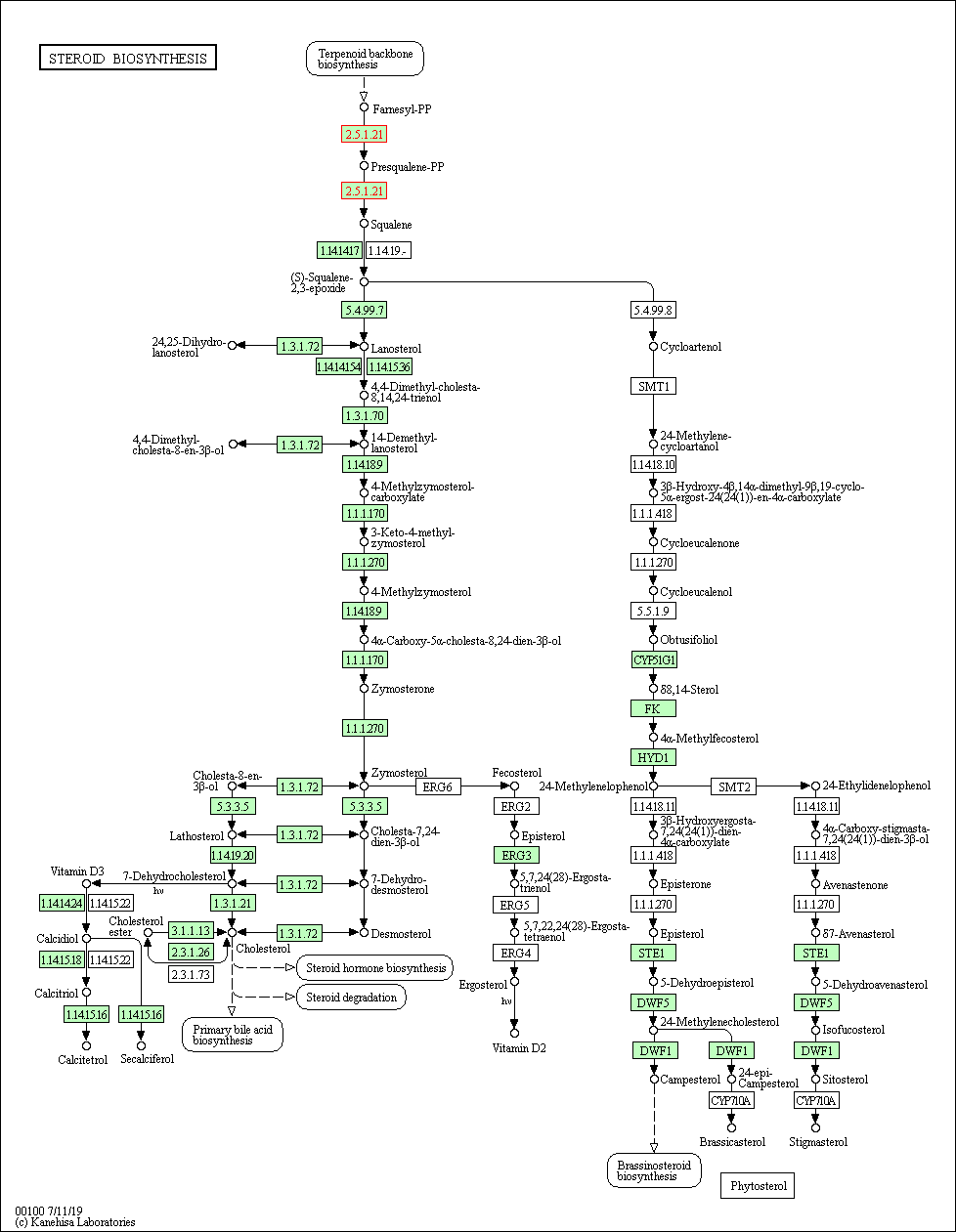
Pathway MAP
|
|
| In-vitro Model | Candida albicans SC5314 | Microorganism model | Candida albicans | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
FAR and FAR/FLC affected fitness of C. albicans biofilm and the ERG gene regulation. | |||||
| Glycyrol | Glycyrrhiza uralensis | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [5] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vivo Model | Mouse was shaved with electric clippers and an approximately 4 cm2 area was marked and slightly abraded with sterile sandpaper before infection with 20 ul of suspension containing 1*106 C. albicans. | |||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
It is very likely that, by damaging the cell wall, glycyrol helps fluconazole invade C. albicans more readily and attack fluconazole's target in the fungus membrane. | |||||
| N-butylphthalide | Apium graveolens | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [6] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| Molecule(s)
Regulation |
Down-regulation | Expression | BICDL1 | Molecule Info | ||
| Down-regulation | Expression | BICDL2 | Molecule Info | |||
| Biological
Regulation |
Up-regulation | ROS accumulation | ||||
| In-vitro Model | Candida albicans | Microorganism model | Candida albicans | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
The synergistic effects between n-butylphthalide and fluconazole potentially relied on the mechanism that n-butylphthalide significantly promoted drug uptake, and suppressed drug efflux via down-regulating the drug transporter encoding genes CDR1 and CDR2. | |||||
| β. A List of Natural Product(s) Able to Reverse the Resistance of This Drug | ||||||
| Alpinia purpurata lectin | Alpinia purpurata | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Reversing Drug Resistance | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa UFPEDA-416 | Microorganism model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa UFPEDA-02 | Microorganism model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
ApuL showed synergistic action in combination with antibiotics. | |||||
| Target and Pathway | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 | Molecule Info | ||
| Candida Cytochrome P450 51 (Candi ERG11) | Molecule Info | [7] | ||