Natural Product (NP) Details
| General Information of the NP (ID: NP0404) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name |
D-cycloserine
|
||||
| Synonyms |
D-cycloserine; cycloserine; 68-41-7; Seromycin; orientomycin; Oxamycin; Cyclo-D-serine; Cyclorin; D-4-amino-3-isoxazolidinone; Cicloserina; Farmiserina; Miroseryn; Tisomycin; Wasserina; Closina; D-4-amino-3-isoxazolidone; alpha-Cycloserine; (+)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone; Cycloserinum; Miroserina; Tebemicina; Novoserin; (R)-4-AMINOISOXAZOLIDIN-3-ONE; (+)-Cycloserine; Oxamicina; (4R)-4-amino-1,2-oxazolidin-3-one; D-(+)-Cycloserine; (4R)-4-aminoisoxazolidin-3-one; PA 94; Cycloserin; Micoserina; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (4R)-; PA-94; (R)-4-AMINO-ISOXAZOLIDIN-3-ONE; D-Oxamycin; RO-1-9213; D-CS; E-733-A; D-4-Amino-3-isossazolidone; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (R)-; (R)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone; HSDB 3218; D-Oxamicina; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, d-; K-300; UNII-95IK5KI84Z; (R)-(+)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone; I-1431; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (+)-; NSC 154851; CHEBI:40009; AI3-50153; D-Cycloserine, synthetic; MFCD00005353; DCS; CHEMBL771; SC-49088; 95IK5KI84Z; CAS-68-41-7; NCGC00016306-01; D-Cycloserine, 98%; Oxamicina [Italian]; Cicloserina [Italian]; DSSTox_CID_2870; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (+)- (8CI); DSSTox_RID_76766; DSSTox_GSID_22870; Cycloserinum [INN-Latin]; Cicloserina [INN-Spanish]; Cycloserine, D-; Closerin; .alpha.-Cycloserine; (R)-Cycloserine; Seromycin (TN); SMR000058313; D-4-Amino-3-isossazolidone [Italian]; R-(+)-Cycloserine; (4R)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone; CYCLOSERINE (D); SR-01000075432; DRG-0195; (R)-(+)-Cycloserine; EINECS 200-688-4; D-amino-3-isoxazolidinone; BRN 0080798; (R)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidone; NSC-76029; cycloserine-(d); Serine, cyclo-; NSC-154851; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, D; R(+)-4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone; Cycloserine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; 4AX; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (R); Cycloserine, D(+); PubChem5763; D-Cycloserine, powder; Spectrum_000860; 1pb9; Prestwick0_001089; Prestwick1_001089; Prestwick2_001089; Prestwick3_001089; Spectrum2_000084; Spectrum3_000371; Spectrum4_000305; Spectrum5_000797; Lopac-C-1159; Lopac-C-3909; Lopac-C-7005; 3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-, (4R)- (9CI); C 3909; C-9390; C-9400; Lopac0_000252; SCHEMBL34322; BSPBio_001138; BSPBio_002121; KBioGR_000890; KBioSS_001340; 4-27-00-05549 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS000758215; MLS001423962; MLS002548887; BIDD:GT0707; D-Cycloserine synth. BP 88; DivK1c_000098; SPECTRUM1500215; SPBio_000008; SPBio_003029; BPBio1_001252; FA6C7F8B-D080-4EA3-978F-1ECFB5A29D09; GTPL9489; Cycloserine (JP17/USP/INN); 4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone, D-; DTXSID8022870; HMS500E20; KBio1_000098; KBio2_001340; KBio2_003908; KBio2_006476; KBio3_001341; NINDS_000098; HMS1571I20; HMS1920C06; HMS2051C15; HMS2091I14; HMS2098I20; HMS2232F03; HMS3259L19; HMS3260D06; HMS3715I14; NJ-21; Pharmakon1600-01500215; (R)-3-Isoxazolidinone, 4-amino-; 4-Amino-3-isoxazolidinone, (R)-; ACT04767; HY-B0030; Tox21_110361; Tox21_500252; BDBM50038178; BDBM50103516; CCG-39705; D-Cycloserine, >=96.0% (NT); LMPK14000007; NSC756712; s1998; ZINC34676245; 4-Isoxazolidinamine, 3-oxo-, (D)-; AKOS015994626; Tox21_110361_1; AC-4721; DB00260; HS-0079; LP00252; MCULE-4212827696; NC00050; NC00676; NSC-756712; SDCCGSBI-0050240.P005; IDI1_000098; SMP1_000167; NCGC00015213-01; NCGC00015213-02; NCGC00015213-03; NCGC00016306-02; NCGC00016306-03; NCGC00016306-04; NCGC00016306-05; NCGC00016306-07; NCGC00016306-08; NCGC00016306-17; NCGC00093713-01; NCGC00093713-02; NCGC00260937-01; CAS-339-72-0; K138; ST075697; SBI-0050240.P004; AB0007232; AB00443920; EU-0100252; (4R)-4-amino-2,4,5-trihydroisoxazol-3-one; C08057; D00877; AB00443920_09; AB00443920_10; 005C353; 101039-EP2295402A2; 101039-EP2301544A1; Q418508; SR-01000759389; SR-01000075432-1; SR-01000075432-2; SR-01000075432-5; SR-01000075432-9; SR-01000759389-4; SR-01000075432-10; F2173-1228; Z1522567171; Cycloserine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Cycloserine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Species Origin | Streptomyces garyphalus ... | Click to Show/Hide | |||
| Streptomyces garyphalus | |||||
| Disease | HIV-associated tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1C60] | Approved | [1] | ||
| Structure |
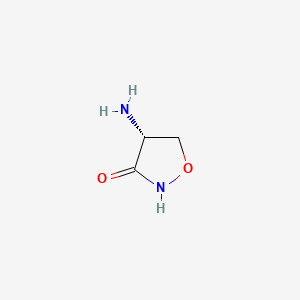
|
Click to Download Mol2D MOL |
|||
| ADMET Property |
Absporption
Caco-2 Permeability
-5.134
MDCK Permeability
-4.51
PAMPA
+++
HIA
- - -
Distribution
VDss
-0.201
PPB
23.4%
BBB
- - -
Metabolism
CYP1A2 inhibitor
- - -
CYP1A2 substrate
- - -
CYP2C19 inhibitor
- - -
CYP2C19 substrate
- -
CYP2C9 inhibitor
- - -
CYP2C9 substrate
- - -
CYP2D6 inhibitor
- - -
CYP2D6 substrate
+++
CYP3A4 inhibitor
- - -
CYP3A4 substrate
- - -
CYP2B6 inhibitor
- -
CYP2B6 substrate
- - -
CYP2C8 inhibitor
- - -
HLM Stability
- - -
Excretion
CLplasma
6.975
T1/2
2.524
Toxicity
DILI
+++
Rat Oral Acute Toxicity
- -
FDAMDD
- - -
Respiratory
- - -
Human Hepatotoxicity
+
Ototoxicity
++
Drug-induced Nephrotoxicity
++
Drug-induced Neurotoxicity
+++
Hematotoxicity
- -
Genotoxicity
+++
Tips: 1. For the classification endpoints, the prediction probability values are transformed into six symbols: 0-0.1 (- - -), 0.1-0.3 (- -), 0.3-0.5 (-), 0.5-0.7 (+), 0.7-0.9 (++), and 0.9-1.0 (+++).
2. Additionally, the corresponding relationships of the three labels are as follows: excellent; medium; poor.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Natural Product | |||||
| Formula |
C3H6N2O2
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1C(C(=O)NO1)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C3H6N2O2/c4-2-1-7-5-3(2)6/h2H,1,4H2,(H,5,6)/t2-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DYDCUQKUCUHJBH-UWTATZPHSA-N
|
||||
| CAS Number |
CAS 68-41-7
|
||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| Combinatorial Therapeutic Effect(s) Validated Clinically or Experimentally | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α. A List of Drug(s) Whose Efficacy can be Enhanced by This NP | ||||||
| Pioglitazone | Acute diabete complication | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This Drug | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vivo Model | Orofacial neuropathic pain mouse model was used in this study. | |||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
The DCS/PIO combination not only attenuated orofacial neuropathic pain and anxiety-related behaviors associated with trigeminal nerve injury, but it also improved mitochondrial bioenergetics. | |||||
| Target and Pathway | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Glutamate receptor ionotropic NMDA 1 (NMDAR1) | Molecule Info | [3] | |
| Mycobacterium alanine racemase (MycB alr) | Molecule Info | [3] | ||
| Mycobacterium D-alanine-D-alanine ligase A (MycB ddl) | Molecule Info | [4] | ||
| KEGG Pathway | Ras signaling pathway | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Rap1 signaling pathway | |||
| 3 | Calcium signaling pathway | |||
| 4 | cAMP signaling pathway | |||
| 5 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | |||
| 6 | Circadian entrainment | |||
| 7 | Long-term potentiation | |||
| 8 | Glutamatergic synapse | |||
| 9 | Alzheimer's disease | |||
| 10 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | |||
| 11 | Huntington's disease | |||
| 12 | Cocaine addiction | |||
| 13 | Amphetamine addiction | |||
| 14 | Nicotine addiction | |||
| 15 | Alcoholism | |||
| 16 | D-Alanine metabolism | |||
| 17 | Peptidoglycan biosynthesis | |||
| 18 | Metabolic pathways | |||
| 19 | Vancomycin resistance | |||
| Panther Pathway | Huntington disease | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Ionotropic glutamate receptor pathway | |||
| 3 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor group III pathway | |||
| 4 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor group I pathway | |||
| 5 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor 1 and 3 signaling pathway | |||
| Reactome | EPHB-mediated forward signaling | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Unblocking of NMDA receptor, glutamate binding and activation | |||
| 3 | CREB phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII | |||
| 4 | Ras activation uopn Ca2+ infux through NMDA receptor | |||
| 5 | RAF/MAP kinase cascade | |||
| WikiPathways | SIDS Susceptibility Pathways | Click to Show/Hide | ||
| 2 | Hypothetical Network for Drug Addiction | |||
| 3 | Neurotransmitter Receptor Binding And Downstream Transmission In The Postsynaptic Cell | |||
| 4 | Spinal Cord Injury | |||
| 5 | BDNF signaling pathway | |||
| 6 | Alzheimers Disease | |||

