Drug Details
| General Information of the Drug (ID: DR9940) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name |
Ciprofloxacin
|
|||
| Synonyms |
ciprofloxacin; 85721-33-1; Ciprobay; Ciprofloxacine; Cipro; Ciproxan; Ciprofloxacina; Cipro IV; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; Ciprofloxacino; Ciprofloxacinum; Ciproflox; Ciproxina; BAY q 3939; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; Cetraxal; Ciloxan; Cipro XR; CPFX; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; Bay-09867; C17H18FN3O3; UNII-5E8K9I0O4U; Ciproxin; Ciflox; BAYQ3939; 1-CYCLOPROPYL-6-FLUORO-4-OXO-7-PIPERAZIN-1-YL-1,4-DIHYDROQUINOLINE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID; 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-; Ciprofloxacin (Cipro); CHEMBL8; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-ylquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; Bay o 9867; 5E8K9I0O4U; Ciprocinol; Cipromycin; Ciproquinol; Bacquinor; Bernoflox; Cifloxin; Ciprinol; Ciprodar; Septicide; CHEBI:100241; Ciprofloxacin-d8; Velmonit; Ciprofloxacin monohydrochloride; MFCD00185755; Ciprofloxacin, 98%; Ciprecu; Ciprogis; Ciprolin; Ciprolon; Ciprowin; Ciproxine; Citopcin; Corsacin; Fimoflox; Ipiflox; Italnik; Otiprio; Probiox; Proflaxin; Quinolid; Quintor; Roxytal; Spitacin; Superocin; Zumaflox; Baflox; Ciplus; Ciriax; Rancif; Cilab; Cixan; Cycin; Loxan; Unex; Sophixin Ofteno; Ciprobay Uro; Alcon Cilox; Bi-Cipro; Cipro (TN); 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-; Proksi 250; Proksi 500; Cyprobay; AuriPro; Eni; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazinylhydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-hexahydro-1-pyrazinyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid; BAY-o 9867; Ciprofloxacine [INN-French]; Ciprofloxacinum [INN-Latin]; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; SMR000471901; Ciprofloxacino [INN-Spanish]; BAY-O-9867; CCRIS 5241; NSC620634; HSDB 6987; SR-05000001863; NCGC00016959-01; CAS-93107-08-5; CIPRO IN DEXTROSE 5% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; BRN 3568352; rubrum; Ciprine; Linhaliq; Bay 09867; CIPRO IN SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.9% IN PLASTIC CONTAINER; Ciprofloxacin,(S); Ciprofloxacin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; Spectrum_000162; 3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-, hydrochloride; Prestwick0_000113; Prestwick1_000113; Prestwick2_000113; Prestwick3_000113; Spectrum2_001567; Spectrum3_001872; Spectrum4_000874; Spectrum5_001089; Cipro (*Hydrochloride*); CBMicro_048498; Ciloxan (*Hydrochloride*); SCHEMBL2900; Oprea1_008239; Oprea1_313572; BSPBio_000126; BSPBio_003344; KBioGR_001567; KBioSS_000642; ANHYDROUS CIPROFLOXACIN; MLS001336035; MLS006011837; BIDD:GT0205; DivK1c_000095; SPECTRUM1503614; SPBio_001474; SPBio_002065; ARONIS020379; BPBio1_000140; DTXSID8022824; BAY-O9867; BDBM21690; GTPL10902; HMS500E17; KBio1_000095; KBio2_000642; KBio2_003210; KBio2_005778; KBio3_002846; Linhaliq [Liposomal Formulation]; ZINC20220; BAY O 9867 FREE BASE; BAY-O-9867 FREE BASE; Ciprofloxacin (JP17/USP/INN); NINDS_000095; Bay o 9867 (*Hydrochloride*); BAY-Q-3939; HMS1922E18; HMS2090O07; HMS2093I03; Pharmakon1600-01503614; ALBB-015909; BCP28586; HY-B0356; RKL10073; BBL005612; CCG-39345; CIPROFLOXACIN EXTENDED RELEASE; Ciprofloxacin, >=98.0% (HPLC); NSC758467; NSC759028; s2027; SBB012554; STK021082; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; AKOS000269653; AC-7613; DB00537; KS-5006; MCULE-8631780654; NSC 758467; NSC-758467; NSC-759028; IDI1_000095; SMP1_000125; NCGC00016959-02; NCGC00016959-03; NCGC00016959-04; NCGC00016959-05; NCGC00016959-07; NCGC00095058-01; NCGC00095058-02; NCGC00178128-01; AK163192; ST024751; SBI-0048462.P003; AB0011928; FT-0601635; A-8526; C05349; Ciprofloxacin 100 microg/mL in Methanol:Water; D00186; J10137; 721C331; Ciprofloxacin, VETRANAL(TM), analytical standard; Q256602; Ciprofloxacin, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; SR-05000001863-1; SR-05000001863-3; BRD-K04804440-311-02-3; Z56933707; Ciprofloxacin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Ciprofloxacin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro 4-oxo-7-[1-piperazinyl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic Acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7- (1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline-carboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3- quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-quinoline -3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1piperazinyl)-3quinolinecarboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-quinoline-3-carboxylic acid; 1-Cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(1-piperazinyl)-4-oxo-3-quinoline carboxylic acid; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-7-(piperazin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid; Ciprofloxacin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-piperazin-1-yl-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid hydrochloride
Click to Show/Hide
|
|||
| Molecular Type |
Small molecule
|
|||
| Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | Approved | [1] | |
| Structure |
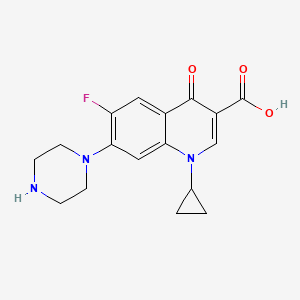
|
Click to Download Mol2D MOL |
||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Natural Product | ||||
| Formula |
C17H18FN3O3
|
|||
| PubChem CID | ||||
| Canonical SMILES |
C1CC1N2C=C(C(=O)C3=CC(=C(C=C32)N4CCNCC4)F)C(=O)O
|
|||
| InChI |
1S/C17H18FN3O3/c18-13-7-11-14(8-15(13)20-5-3-19-4-6-20)21(10-1-2-10)9-12(16(11)22)17(23)24/h7-10,19H,1-6H2,(H,23,24)
|
|||
| InChIKey |
MYSWGUAQZAJSOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|||
| CAS Number |
CAS 85721-33-1
|
|||
| ChEBI ID | ||||
| TTD Drug ID | ||||
| DrugBank ID | ||||
| Combinatorial Therapeutic Effect(s) Validated Clinically or Experimentally | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α. A List of Natural Product(s) Able to Enhance the Efficacy of This Drug | ||||||
| Fosfomycin | Streptomyces fradiae | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [2] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Shigella flexneri isolates | Microorganism model | Shigella flexneri | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Against CIPR S. flexneri isolates, the CIP/FOS combination induced synergy, and increased bacterial killing in vitro and in a simple invertebrate model of infection. | |||||
| L-methionine | Chenopodium quinoa | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [3] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA01 | Microorganism model | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |||
| In-vivo Model | Mice with PA pneumonia were used as animal model in this study. | |||||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
Intranasal L-Met treatment along with antibiotics can cure chronic PA lung infection in mice. | |||||
| Zinc oxide | Zincite | Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Data of This NP | ||||
| Achieving Therapeutic Synergy | Click to Show/Hide | |||||
| Representative Experiment Reporting the Effect of This Combination | [4] | |||||
| Detail(s) |
Combination Info
 click to show the detail info of this combination
click to show the detail info of this combination
|
|||||
| In-vitro Model | A. baumannii | Microorganism model | Acinetobacter baumannii | |||
| Experimental
Result(s) |
ZnO-NPs potentiate the antimicrobial action of ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime. | |||||
| Target and Pathway | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target(s) | Bacterial DNA gyrase (Bact gyrase) | Molecule Info | [5] | |
| Bacterial Penicillin binding protein (Bact PBP) | Molecule Info | [6] | ||

